If you’re already up-to-speed on the differences between RAID 0 & 1, RAID 1 & 5, and RAID 5 & 6 then this one’s for you! Our previous articles provide an in-depth look at hardware vs software controllers – but now it’s time to learn about a deeper dive into how two of the most popular configurations (RAID 5 and 10) compare. Discover their individual strengths/weaknesses as well as when they should be applied in real-world scenarios so that your data is always kept secure!

Quick Recap: What Is RAID?
RAID 5 and RAID 10 are powerful data storage systems known for their impressive fault tolerance and redundancy. By combining multiple hard drives into one virtual unit, RAID setups offer users varying levels of protection against degradation or loss of important files. This comparison post dives deep into the two most popular configurations – RAID 5 with its parity checks to ensure maximum resilience, as well as raid 10 which utilizes mirroring technology to preserve vital information in times of crisis.
What Is RAID 5
RAID 5 provides the ultimate storage solution, using a combination of hard disks to ensure your data is always safe. By ‘striping’ information and parity data evenly across multiple disk drives – which operate in parallel with one another – RAID 5 creates powerful redundancy that can quickly recover from any lost or failed components. Your valuable assets are now safeguarded within an impenetrable fortress!
Example
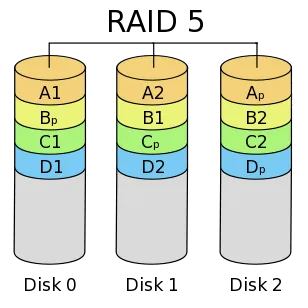
In its minimal setup, a RAID 5 array uses three hard disks and distributes data based on the user’s preference. Let’s say you prefer splitting files in half, and load your array with three, equally sized files labeled “A”, “B” and “C”. Your array would look something like this:
| Disk 1 | Disk 2 | Disk 3 |
| File A1 | File A2 | Parity A |
| File B1 | Parity B | File B2 |
| Parity C | File C1 | File C2 |
Using this setup, we sacrifice space equal to one hard disk to secure the data on every hard disk. As you can see, if any one drive fails, either the files are untouched, or the parity data remains to rebuild what is lost.
Advantages of RAID 5
- The read speed for RAID 5 is fast.
- Comes with data redundancy due to parity.
- The setup is stable.
- A failed drive can be rebuilt on time.
- A good amount of storage space.
- Drives can be hot-swapped to prevent downtime.
Disadvantages of RAID 5
- All data is lost if two drives fail simultaneously.
- The parity drive makes write speeds slower.
- Data restoration can be slow.
- The setup can be complex for those new to RAID configurations
What Is RAID 10
RAID 10 is an advanced data storage solution that offers speed and reliability. It combines the power of RAID 0’s disk striping with the security of mirror drives used in RAID 1 – making two exact copies of each drive, stored on separate mirrored disks for protection against catastrophic failure or corruption. However, it requires a minimum setup using 4 individual drives which must be added as pairs to ensure optimal performance; thus allowing users to enjoy faster loading times while also safeguarding their precious files from potential disaster!
Example
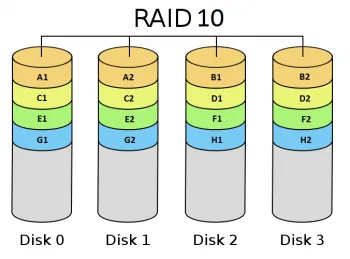
With a RAID 10 setup, you can achieve the highest level of data protection and performance. It requires at least four hard drives – two that are used to store your data in an efficient way (striping), while the other two create backups to keep it safe from any mishaps (mirroring). By combining these technologies into one system, you get ultimate reliability and speed for whatever task is thrown its way!
| Storage Disk 1 | Storage Disk 2 |
| File A1 | File A2 |
| File B1 | File B2 |
| Mirror Disk 1 | Mirror Disk 2 |
| File A1 | File A2 |
| File B1 | File B2 |
RAID 10 gives you the best of both worlds – get double your storage capacity compared to a single drive with half, but replace failed drives quickly and have almost lightning-fast read speeds. It’s an ideal solution for those needing greater data protection and speed!
Advantages of RAID 10
- The high-speed performance of this system is truly remarkable –
- reads and writes occur almost instantaneously due to operations running in tandem on separate drives.
- No disruption will be experienced during maintenance, as new disks can easily replace old ones at any time.
- Furthermore, should a failure arise the system recovers incredibly quickly since its high fault tolerance allows it to tolerate multiple disk collapses.
Disadvantages of RAID 10
Despite its high cost, this storage solution is far from optimized due to ineffective mirroring techniques.
RAID 5 vs RAID 10 Comparison Chart
| RAID 5 | RAID 10 | |
| Basic Function/Key Feature | Disk Striping With Parity Check System | Combines Disk Striping With Mirroring |
| Storage Disks Required | 3 or More | 4 |
| Storage Capacity | 60-75% or 1 Drive Worth of Space is Lost | 50% |
| Parity Check System | Yes – Parity – Single Disk | No Parity Check System |
| Fault Tolerance | Yes – 1 Drive Can Fail | Multiple Drives Can Fail |
| Data Recovery | Yes – Using the Parity Check System | Yes – 100% Redundancy |
| Overall Cost | Expensive | Very Expensive |
| Disk Read Performance | Fairly Quick | Fantastic Performance |
| Disk Write Performance | Slow | Excellent Performance |
| Write Penalty? | Yes – Slightly Due to Writing to the Parity Block | No. |
| Appropriate Purpose | A Balance Between Speed & Data Security | When You Need Fast Read/Write Speeds & Fast Failure Recovery |
RAID 5 vs RAID 10 Critical Distinctions
- RAID 5 and RAID 10 offer different storage strategies: the former stripes data with an extra parity bit, while the latter combines disk striping for performance benefits with mirroring for redundancy.
- RAID 5 is economical because it only requires 3 hard drives, while RAID 10 utilizes a minimum of 4. Furthermore, when expanding on your storage capacity with the latter format you must do so in pairs for optimal performance.
- RAID 5 packs a powerful punch when it comes to storage capacity. It can handle the loss of one disk without compromising up to half its total capacity, unlike RAID 10 which loses half with just one failed drive.
- With RAID 5, a single disk failure won’t cause data loss; but with the more powerful RAID 10 setup, up to three disks can fail before your critical information is in jeopardy – unless all drives of one pair are lost.
- RAID 10 stands out for its powerful combination of speedy read and write capabilities, while RAID 5 only offers fast reads.
Use Cases: When to Use RAID 5 in Real-Life Scenarios
RAID 5 is an ideal option for those seeking to maximize data performance, security, and capacity in a single solution. It can be particularly effective when used in contexts such as gaming PCs requiring large amounts of storage or business operations where uninterrupted access to crucial information needs are vital.
- Are you strapped for cash but seeking reliable fault tolerance without compromising storage or performance? Look no further – the perfect solution is here!
- To keep up with your data demands, you need an archive, application, or file server that can handle massive storage needs. Maximize efficiency by inves
- With a quality high-availability solution, such as a news server, and the right hardware setup for small to medium businesses with servers that are limited to 3 – 16 drives, you have everything needed for reliable operation. Make sure your system is up and running day and night so that customers can quickly access data or submit orders whenever they need it! ting in a system capable of meeting all your capacity requirements!
Use Cases: When to Use RAID 10 in Real-Life Scenarios
RAID 10 is the perfect match for scenarios that demand top-tier fault tolerance and accelerated read/write speeds; tasks like I/O intensive applications can all be handled with ease. Whether it’s an online database or a major streaming service, RAID 10 has what you need to make sure performance stays at its peak!
- Email servers can be challenging beasts to tame, often requiring deft management of huge data reserves. Through careful collection and storage techniques, it’s possible to make sure your emails remain both secure and accessible whenever they’re needed!
- Powerful web hosting servers, capable of handling an influx of requests and delivering speedy responses to a vast number of users simultaneously.
- Ensuring continuous access is essential, and the best way to do this is by implementing a database system with minimal down-time. This can be difficult when depending on technology but investing in an efficient solution pays off greatly!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Is RAID 5 Not Recommended Over RAID 10?
RAID 5 may seem like a cheaper alternative, however, it is not the most secure option. Without mirroring or redundancy built in, one failed hard drive disk can spell disaster for your array and complicate data recovery efforts. RAID 10 on the other hand provides 100% redundancy allowing you to rest easy knowing that no matter what happens there will always be backup available – plus its performance edges out RAID 5 as well!
Is Performance Better in RAID 10 than in RAID 5?
RAID 10 is a powerful combination of disk striping and mirroring- providing the best performance, fault tolerance, and data security from its combined RAID 0 & 1 features. This makes it an ideal choice for those who require maximum protection against system failure or wish to maximize their storage speed!
How Many Hard Drives Do You Need in RAID 5 vs. 10?
RAID 5 is an ideal configuration for those who need protection and storage, requiring a minimum of three hard drives to function. Just add one more drive for added reliability with RAID 10! This setup ensures top-notch data security and performance – all from four fantastic drives at the same time.
Do I Need to Back My Data Up If Using RAID?
RAID may be a great way to protect your data from drive malfunctions, but it should never substitute for successful backups. Even if you have the most secure RAID setup imaginable, any type of hard drive failure can still lead to complete dataset loss – so make sure that traditional forms of backup are always in place!
Wrapping It Up
RAID 5 and RAID 10 are two distinctly different ways to protect your data. While RAID 5 builds a safety net by collecting Parity Data, RAID 10 creates an extra layer of security with duplication – every piece of information is cloned for maximum protection but at the cost of halving its total storage capacity.
